Smart Lights
-

How to Set Up Philips Hue Bridge
The Philips Hue Bridge serves as the central hub for the Hue smart lighting ecosystem. Without the Bridge, Bluetooth control…
Read More » -

Best Smart Bulbs for Alexa and Google Assistant: from Cheap to Expensive
Smart bulbs have transformed everyday lighting into a dynamic, voice-activated experience for seamless control through assistants like Alexa and Google…
Read More » -

Best Outdoor Lights for Any Outdoor Space
The allure of smart outdoor lighting transcends mere illumination. It’s about transforming your exterior spaces into dynamic environments that blend…
Read More » -

The Best Smart Switches 2025: Best Dimmers and Buttons For Your Smart Home Devices
Transform your home into a beacon of modern convenience with the best smart home switches of 2025! While screwing in…
Read More » -

A Complete Guide to Modern Dining Room Lights
Your modern dining room lights bathe the space in just the right glow, where family dinners linger longer and laughter…
Read More » -

Nanoleaf Rope Light Review 2025: Smart, Flexible & Bright
Smart lighting options like the Nanoleaf Matter Smart Multicolor Rope Light bring flexibility and innovation to home decor. This product…
Read More » -

Best Light Bulbs for Applying Makeup | Perfect Lighting for a Flawless Look
Applying makeup requires precise visibility of skin tones and product shades to achieve a flawless finish. Proper lighting reveals true…
Read More » -

Best Cheap Smart Light Bulbs (2025): Affordable Smart Lighting That Works
Smart light bulbs don’t have to break the bank to make your home feel modern. In 2025, these best affordable…
Read More » -

Govee Wi Fi LED Bulb Review (2025): Smart, Affordable, and Feature-Rich
Govee Wi Fi LED Bulbs offer an easy and instant way to enhance the atmosphere of any room. Simply screw…
Read More » -

Philips Hue Review
Philips Hue stands as the gold standard in smart lighting, transforming how we illuminate and interact with our living spaces.…
Read More » -

Philips HuePlay Light Bar Review 2025: Bright, Smart & Bold
In this Philips Hue Play Light Bar review, transform your entertainment space with the philips hueplay, a smart lighting solution…
Read More » -

Philips Hue Bridge Review (2025): Features, Setup Guide & Is It Worth It?
In an era where smart homes are evolving from novelty to necessity, the Philips Hue Bridge stands as the indispensable…
Read More »
Remember when flipping a light switch was all it took to light up a room? Those simple on-and-off moments now feel like a thing of the past. Today, smart lighting has completely changed the way we live, not just in how we light our homes, but in how we experience light itself. Imagine lights that welcome you when you walk in the door, or bulbs that shift from bright, energizing blue in the morning to a cozy, warm amber as you settle down with a good book. What once seemed like futuristic tech is now a practical, everyday part of many homes.
As we spend more time indoors, smart lighting couldn’t have arrived at a better time. It’s not just about convenience, it can actually boost our wellbeing, improve security, and even help regulate our sleep. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about smart lighting: how it works, the benefits, the challenges, and what the future holds.

Introduction to Smart Lighting
Smart lighting refers to lighting technology that allows users to control illumination wirelessly and automatically through various devices and triggers. Unlike traditional lighting systems, smart lights for homes contain embedded chips enabling them to communicate with smartphones, hubs, and voice assistants. These intelligent fixtures can be programmed, scheduled, and controlled remotely, transforming ordinary illumination into responsive environmental elements that adapt to your lifestyle and preferences.
The Evolution of Smart Home Lighting
The journey from primitive fire to intelligent illumination represents one of humanity’s most significant technological evolutions. Prehistoric humans relied on fire for light, while the 19th century saw revolutionary changes with gas lamps appearing in 1807, dramatically transforming urban environments. The true electrical lighting revolution began in 1879 when Thomas Edison perfected the incandescent bulb, making electric lighting practical for mass adoption.
The 20th century introduced fluorescent lighting in the 1930s, followed by halogen lamps in the 1950s, each offering improvements in efficiency and performance. The development of LED technology in the late 20th century was marked by Nick Holonyak Jr.’s invention of the first practical visible-spectrum light-emitting diode in 1962, which emitted red light using a gallium arsenide phosphide alloy.
This foundation enabled the 21st century’s smart lighting system revolution, where connectivity and intelligence have transformed simple illumination into networked, responsive systems that adapt to our needs and preferences.

Technologies Behind Smart Lighting
The question arises here: what technologies are behind smart lighting systems?
Internet of Things (IoT) in Lighting
The Internet of Things forms the backbone of modern smart lighting systems. Each smart bulb essentially becomes a networked device capable of communicating with other IoT elements in your home. This connectivity enables unprecedented functionality, from real-time monitoring of burnt-out fixtures to automatic adjustments based on environmental conditions. As IoT technology continues advancing rapidly, connecting each individual luminaire to the internet becomes increasingly economical, opening new possibilities for intelligent light management across residential and commercial applications.
Role of Sensors and Connectivity
Sensors represent the “eyes and ears” of any smart lighting system, enabling automated responses to environmental changes. Motion detectors activate lights when someone enters a room and deactivate them when the space is vacant. Ambient light sensors measure natural daylight levels, allowing smart light fixtures to adjust brightness accordingly, maintaining optimal illumination while conserving energy.
Temperature and humidity sensors can even modify lighting scenarios based on weather conditions, while occupancy patterns over time can inform predictive lighting behaviors that anticipate your needs before you even reach for a switch.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are transforming smart home lighting from responsive to truly intelligent systems. Modern smart lighting control systems can analyze usage patterns to predict preferences, automatically adjusting illumination based on the time of day, activities being performed, or even inhabitants’ moods.
Machine learning enables your lighting system to recognize patterns in your behavior. Gradually learning that you prefer warmer tones in the evening, brighter illumination for cooking, or subdued lighting during movie nights, and automatically implementing these preferences without explicit programming.
- Related Article:
- Roku Smart Bulb SE Color Review
- Philips Hue Play Wall Washer Review
Wireless Protocols (e.g., Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth)
At the core of every smart lighting system lies its wireless communication protocol, an unseen but essential foundation. Each technology offers distinct advantages:
- Zigbee operates on a 2.4 GHz frequency band using mesh networking with low power consumption, making it ideal for large-scale automation and commercial buildings.
- Z-Wave functions on sub-1 GHz frequencies with mesh networking and low power requirements, perfectly suited for secure smart home applications.
- Wi-Fi smart light bulbs provide high-speed communication and seamless cloud integration but consume more power than alternatives.
Bluetooth-enabled smart light bulbs offer direct device control with medium power consumption, while Thread provides an IP-based protocol designed for secure, low-power, and highly scalable communication that integrates well with existing smart home ecosystems.

Key Components of a Smart Lighting System
Every smart system for lighting consists of many key components that are described here:
Smart Bulbs and Fixtures
The foundation of any lighting system begins with the bulbs and fixtures themselves. Smart light bulbs contain wireless chipsets that enable connectivity and control, available in various form factors including standard A19 bulbs, candelabras, flood lights, and specialized shapes.
Premium options like Philips Hue smart lights offer millions of colors and tunable white temperatures, while budget-friendly alternatives like IKEA smart light products provide basic functionality at affordable price points. For integrated solutions, light fixtures incorporate intelligence directly into ceiling fans, pendant lights, and recessed lighting, eliminating the need for separate bulb replacements.
- Related Article:

Smart Switches and Dimmers
While smart bulbs offer tremendous flexibility, smart control through dedicated switches and dimmers provides a familiar interface for those accustomed to traditional wall controls. Companies like Lutron smart lighting have transformed the humble light switch into sophisticated control panels available in various colors and finishes that seamlessly blend with home décor.
These devices can control multiple lights simultaneously, activate pre-programmed scenes, and integrate with other smart home functions while maintaining the intuitive simplicity of physical controls that everyone understands.
Lighting Control Hubs and Apps
The command center of your lighting system typically consists of a dedicated hub and smartphone application. Hubs like those required for Philips smart light systems serve as translators between your home network and proprietary lighting protocols, enabling sophisticated automation and remote access.
Mobile applications provide intuitive interfaces for controlling individual lights, grouping fixtures into rooms or zones, creating custom scenes, and programming schedules. Many systems also offer web interfaces for management from computers, ensuring you can always control your illumination regardless of which device you’re using.
Motion and Ambient Light Sensors
Sensors transform passive lighting systems into responsive environments. Motion detectors can trigger smart lights Alexa compatible fixtures when you enter a room and turn them off when you leave, eliminating wasted energy. Ambient light sensors measure natural daylight, allowing your lighting system to automatically dim artificial illumination when sufficient sunlight is available, then gradually increase brightness as evening approaches.
Temperature sensors can adjust color temperature to complement the weather, while occupancy sensors distinguish between momentary movements and sustained presence, preventing false triggers that would otherwise cause annoying on/off cycles.

Integration with Voice Assistants (Alexa, Google Assistant, Siri)
Voice control represents perhaps the most intuitive way to interact with smart light environments. Smart light bulb Alexa compatibility allows for simple commands like “Alexa, turn on the kitchen lights” or complex requests such as “Alexa, set movie night scene.” Similarly, smart lights Google Home integration enables convenient hands-free control using Google’s assistant.
For Apple enthusiasts, Apple smart lights using HomeKit technology respond seamlessly to Siri commands across iPhones, iPads, Macs, and HomePods. This voice integration transforms lighting control from a physical action to a conversational interaction that feels remarkably natural and convenient.
Benefits of Smart Lighting
If you’re still not convinced about how smart lighting is changing our lives, wait to see what benefits this technology has to offer:
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the most compelling advantages of smart home lighting is its potential for significant energy conservation. LED-based smart light bulbs already consume up to 75% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs while lasting up to 50,000 hours; approximately 20 times longer than halogen alternatives.
When enhanced with intelligent controls, these efficiency gains multiply. Occupancy sensors ensure lights operate only when needed, while daylight harvesting automatically dims artificial lighting when natural light is sufficient. Scheduling features can automatically implement energy-saving settings during peak rate periods, and the ability to remotely verify that all lights are off eliminates wasteful operation when spaces are unoccupied.

Customization and Mood Setting (Color, Brightness, Scheduling)
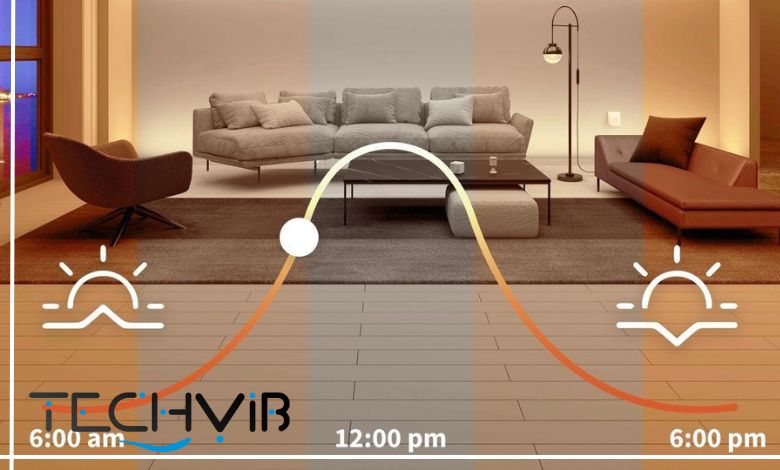
Smart systems for lighting transform static illumination into dynamic elements that enhance your living experience. Products like RGB smart light bulbs offer millions of colors for setting the perfect ambiance for any occasion. Color-tunable smart bulbs can mimic natural daylight patterns, transitioning from energizing cool white in the mornings to calming warm white in the evenings, supporting your body’s natural circadian rhythms. Programmable scenes allow you to instantly transform environments with presets for dining, entertaining, movie watching, or reading.
Automation and Convenience
Automation eliminates the tedious task of manually adjusting multiple lights throughout your home. Smart lighting can automatically activate when you arrive home by detecting your smartphone’s presence, gradually wake you with simulated sunrise effects, or guide nighttime pathways with subtle illumination triggered by motion. For families with children, bedtime routines can automatically implement progressive dimming schedules that signal approaching sleep times without constant parental reminders.
- Related Article:
- smart speakers
- Smart Locks and Entry
- smart display
- smart home
Enhanced Home Security (presence simulation, motion-activated lights)
Smart home lighting significantly enhances home security through several intelligent features. Presence simulation can make vacant homes appear occupied by reproducing realistic lighting patterns based on your typical usage. With lights activating in different rooms throughout evening hours, deterring potential intruders.
Motion-activated outdoor smart lighting immediately illuminates when unexpected movement is detected, potentially startling intruders while simultaneously recording activity through integrated security cameras. Integration with security systems allows lights to flash during emergencies, guiding occupants to exits during fire alarms or attracting attention when security breaches occur.

Challenges and Limitations
Every good thing comes with challenges and smart lighting is no exception.
High Initial Setup Costs
Despite falling prices, implementing comprehensive lighting systems often requires significant initial investment. Premium best smart light bulbs like Philips Hue can cost $40-60 per bulb, while even budget options like Atomi smart lights typically exceed $15 each, considerably more than traditional incandescent or basic LED alternatives. Full-home systems requiring dozens of bulbs, dedicated hubs, and compatible switches can quickly escalate into thousands of dollars.
While energy savings eventually offset these costs, the extended payback period remains prohibitive for budget-conscious consumers, especially when considering the rapid evolution of technology that may render current investments obsolete before recouping their costs.
Compatibility Between Brands and Platforms
The lack of universal standards creates frustrating compatibility challenges within the lighting ecosystem. Best smart lights for Alexa might not work with Google Home, while smart lights for Google Home may require different hubs than HomeKit-compatible devices. Even within single ecosystems, functionality varies tremendously. Some third-party bulbs support basic on/off control but lack color or temperature adjustment capabilities.
Consumers must carefully research compatibility before purchases or risk creating fragmented systems requiring multiple apps and hubs. While standardization efforts like Matter promise future interoperability, current market fragmentation forces difficult choices between ecosystem commitment and best-in-class features.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Connected smart light fixtures create potential privacy and security vulnerabilities that traditional lighting never presented. Each networked bulb represents another potential entry point for hackers, particularly concerning budget brands implementing minimal security protocols. User data collection raises additional privacy concerns, as lighting usage patterns can reveal sensitive information about home occupancy, sleep schedules, and daily routines.
Even legitimate manufacturers may collect operational data that reveals more about your lifestyle than you might realize. To reduce potential risks, it is essential to carefully review manufacturer privacy policies, keep firmware updated regularly, and ensure network configurations are secure.
Dependence on Stable Internet Connection
Stable internet connectivity is crucial for the optimal performance of most smart lighting systems. While basic on/off control typically works locally, advanced features often require cloud services, rendering sophisticated automation, remote access, and voice control inoperable during internet outages.
Even systems advertising local control frequently need internet access for firmware updates, time synchronization, and specialized features. This dependence creates vulnerability during connectivity disruptions, potentially leaving users unable to control lights through apps while simultaneously disconnecting from traditional manual switches. Truly resilient systems require careful planning with fallback mechanisms for inevitable connectivity interruptions.
The Future of Smart Lighting
After all of the benefits and challenges, what does the future of smart lighting for homes hold for the world?
Trends like Human-Centric Lighting (HCL)
Human-centric lighting represents a revolutionary approach focused on supporting natural biological processes through intelligent illumination. Advanced lighting systems now mimic natural daylight patterns, automatically adjusting color temperature to support circadian rhythms. Premium systems like Ketra (owned by Lutron smart lighting) offer near-infinite spectral control, recreating natural light with unprecedented accuracy while dimming to levels as low as 0.01%.
Future developments will likely incorporate personalized biological profiles, adjusting lighting to individual chronotypes, seasonal affective responses, and even specific health conditions requiring specialized light therapy interventions.

Integration with Smart Cities and IoT Ecosystems
The future of smart lighting extends far beyond residential applications into comprehensive urban infrastructure. Smart lighting industries are developing technologies that transform ordinary streetlights into multifunctional assets. They incorporate environmental sensors, traffic monitoring cameras, public Wi-Fi access points, and electric vehicle charging stations.
These integrated systems will collect valuable data for municipal planning while dynamically adjusting illumination based on pedestrian activity, weather conditions, and special events. The resulting networks will form the backbone of smart city initiatives, creating intelligent urban environments that respond in real-time to changing conditions while optimizing energy usage and enhancing public safety.
Adaptive and Context-Aware Lighting
Truly intelligent smart lighting control is evolving from programmed responses to genuine contextual awareness. Next-generation systems will automatically recognize activities being performed in spaces through advanced sensor arrays and machine learning algorithms, adjusting illumination appropriately for cooking, reading, exercising, or entertaining without explicit commands.
Environmental factors like exterior weather conditions will influence interior lighting, while emotional recognition may eventually allow systems to detect stress or fatigue and adjust lighting to support well-being. This contextual intelligence will transform lighting from a manually controlled element to an anticipatory environmental factor that seamlessly adapts to human needs.
Advancements in AI-based Lighting Automation
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming smart lighting systems from programmable to truly predictive technologies. Advanced machine learning algorithms analyze occupancy patterns, usage histories, and environmental factors to anticipate lighting needs before users even realize them. Wireless smart light systems will eventually recognize individual family members through smartphone presence, wearable devices, or biometric identification, which automatically implement personalized lighting preferences without explicit selection.
Sophisticated neural networks will continuously optimize energy usage while maintaining preferred illumination levels, potentially reducing consumption by 30-40% beyond current capabilities while simultaneously improving user satisfaction through anticipatory adjustments that seem almost prescient.
The Best Smart Lighting Reviews
When exploring smart systems for lighting environments, consumers face overwhelming choices across price points and ecosystems. Philips Hue smart lights consistently dominate premium categories with unmatched color accuracy, robust ecosystem integration, and exceptional reliability though their higher price points and hub requirements present barriers for casual users.
Value-conscious shoppers often gravitate toward Govee smart lights offering impressive color rendering and innovative products like Govee light bars at substantially lower costs. For unified whole-home solutions, Lutron lighting provides unparalleled reliability with professional-grade performance, while tech enthusiasts frequently explore artistic options like Nanoleaf smart lights with modular hexagon smart lights and programmable effects for statement installations that double as functional illumination.

Conclusion
Home lighting has evolved from simple remote-controlled bulbs to sophisticated systems that transform how we experience and interact with our living environments. While challenges remain regarding cost, compatibility, and privacy, the trajectory toward increasingly intelligent, contextual, and human-centric lighting seems inevitable. As you consider implementing smart lights for home use, carefully evaluate your specific needs, existing smart home ecosystem, and budget constraints to select the system that best aligns with your lifestyle.





